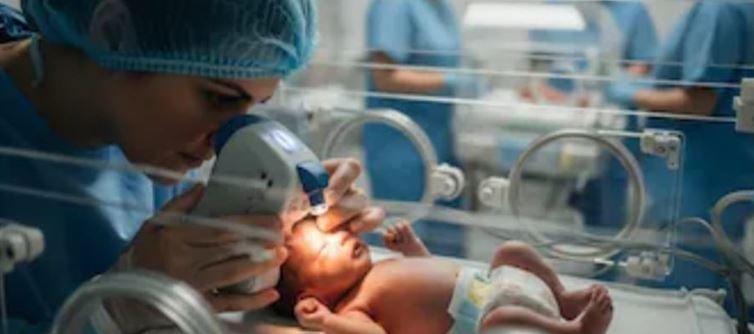
Premature delivery is defined as birth before 37 weeks of pregnancy.
Despite improved medical facilities, the incidence of preterm births in india is steadily increasing.
Globally, preterm birth rates range from 4% to 15%, while in india, they are around 10% to 15%.
India records 2.5 to 3 million premature births annually, the highest in the world, due to its large population and uneven healthcare access.
Why Premature Births Are Increasing
There is no single cause; multiple factors contribute to premature delivery.
Key risk factors include:
Maternal age: very young pregnancies and pregnancies after 35 increase risks.
Short gaps between pregnancies put physical stress on the mother.
Maternal nutrition: anemia, low BMI, and vitamin deficiencies significantly raise the risk.
Chronic health conditions: diabetes, thyroid issues, high blood pressure, and obesity.
Lack of regular checkups: undetected infections or health problems can trigger premature labor.
Infections: often ignored due to embarrassment or lack of awareness.
Stress and lifestyle factors: inadequate sleep, poor diet, and insufficient physical activity.
Steps to Reduce the Risk of Premature Birth
Start early: adolescent girls should receive proper nutrition, vaccinations, and reproductive health education.
Pre-conception screening: correct anemia, treat infections, and manage thyroid or other conditions.
Regular prenatal checkups: monitor blood pressure, sugar levels, baby’s growth, and placental health.
Balanced diet: includes iron, folic acid, calcium, protein, and omega-3 fatty acids.
Healthy lifestyle: gentle exercise, prenatal yoga, adequate sleep, and proper hydration.
Stress management: maintain emotional well-being throughout pregnancy.
Conclusion
While not all premature births can be prevented, timely care, awareness, and healthy habits can significantly reduce the risk.
Early intervention, nutrition, and regular monitoring remain key strategies for safer pregnancies in India.
Disclaimer:
The information contained in this article is for general informational purposes only. While we strive to ensure accuracy, we make no warranties or representations of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability of the content. Any reliance you place on the information is strictly at your own risk. The views, opinions, or claims expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of any organization mentioned. We disclaim any liability for any loss or damage arising directly or indirectly from the use of this article.




 click and follow Indiaherald WhatsApp channel
click and follow Indiaherald WhatsApp channel