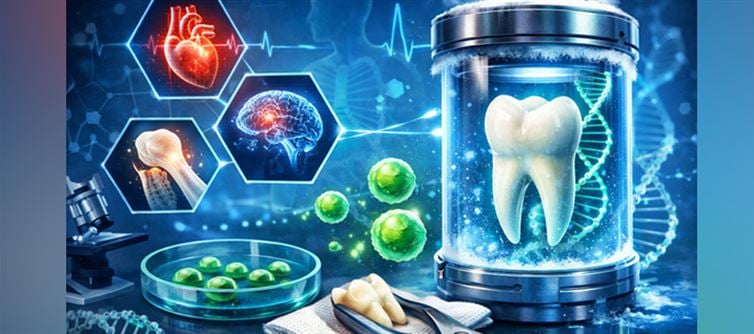
The Tooth You Threw Away Might Have Been a Lifeline
For decades, wisdom teeth were treated like biological leftovers — painful, problematic, and promptly discarded. Out they came in adolescence. Into the medical waste bin they went.
But what if those molars weren’t useless at all?
What if they were biological treasure chests — packed with stem cells capable of repairing bone, regenerating tissue, and potentially reshaping the future of medicine?
Science is now forcing a rethink.
1️⃣ The Stem Cell Vault Inside Your Mouth
Wisdom teeth contain dental pulp — soft tissue at the center of the tooth. Inside that pulp are mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), a type of adult stem cell known for their ability to differentiate into multiple tissue types.
Research summarized in journals such as Journal of Natural Science, Biology and Medicine highlights that dental stem cells can transform into:
• Bone cells
• Cartilage cells
• Muscle tissue
• Nerve-like cells
• Fat cells
Unlike embryonic stem cells, these are adult stem cells — meaning fewer ethical controversies and a lower risk of immune rejection when used autologously (from the same individual).
The key phrase here: potential.
2️⃣ Why Dental Stem Cells Are So Attractive
Traditional stem cell harvesting — such as bone marrow extraction — can be invasive and uncomfortable.
Wisdom tooth extraction? It’s already happening.
No additional surgery. No added discomfort beyond the planned procedure. If preserved properly, dental pulp stem cells can be cryogenically stored for future use.
In theory, it’s like biological insurance.
A small tissue sample today. A potential regenerative tool tomorrow.
3️⃣ What the Research Actually Shows
Preclinical studies and early research suggest dental stem cells may support therapies for:
• Bone regeneration in orthopedic injuries
• Periodontal and jaw repair
• Cartilage repair in arthritis
• Experimental treatments targeting diabetes
• Neurodegenerative disease models such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s
But here’s the crucial distinction: most of these applications are still in experimental or early clinical phases.
Promising? Yes.
Widely available life-saving treatments? Not yet.
The science is evolving — not finished.
4️⃣ Regenerative Medicine: Hype vs. Horizon
Regenerative medicine aims to repair, replace, or regenerate damaged tissues using biological mechanisms — including stem cells.
Dental stem cells are attractive because:
• They proliferate rapidly in laboratory settings
• They show multipotent differentiation capacity
• They are relatively easy to collect and preserve
However, large-scale, long-term human trials are still required before these therapies become standard medical practice for systemic diseases like heart failure or Parkinson’s.
The leap from petri dish to patient is enormous.
5️⃣ Should You bank Your Wisdom Teeth?
Stem cell banking services now offer preservation options after extraction. The pitch is compelling: future-proof your health.
But there are factors to weigh:
• Cost of collection and long-term storage
• Regulatory approval of future treatments
• Likelihood that autologous stem cells will be required versus donor sources
• The pace of technological advancement
It’s an investment in possibility, not a guaranteed therapy.
The Bottom Line
Your wisdom teeth are no longer just evolutionary leftovers.
They are biological materials with documented regenerative potential. Research supports their versatility in laboratory and preclinical settings. Early-stage applications in regenerative dentistry are already underway.
But the dramatic claim — “they could save your life” — belongs more to the future than the present.
The science is real.
The potential is significant.
The revolution is still in progress.
The next time someone calls wisdom teeth useless, you might want to remind them:
Sometimes the most overlooked parts of the body hold the most unexpected promise.




 click and follow Indiaherald WhatsApp channel
click and follow Indiaherald WhatsApp channel