In today’s world, the internet has become an essential part of everyday life, and Wi-Fi plays a crucial role in making internet connectivity wireless, convenient, and accessible in homes, offices, cafes, and public spaces. But how exactly does Wi-Fi work without using wires, and why is it so reliable? Many people are unaware of the technology behind Wi-Fi, but understanding it is easier than you might think.
Here's a breakdown of how Wi-Fi works and why it’s a game-changer for modern connectivity:
1. What Is Wi-Fi?
Wi-Fi stands for Wireless Fidelity, and it is a wireless networking technology that allows devices like smartphones, laptops, tablets, and smart TVs to connect to the internet or local area networks (LANs) without needing physical cables.
Wi-Fi uses radio waves (similar to how FM radio broadcasts work) to transmit data between your device and a router, which is connected to the internet via a physical cable (usually a fiber optic or broadband connection).
2. The Role of Radio Waves
Radio waves are a form of electromagnetic radiation that can travel through air, walls, and other obstacles, making them ideal for transmitting signals over distances without physical wires.
· Electromagnetic Spectrum: Wi-Fi signals typically operate in two frequency bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. These are part of the radio frequency spectrum.
o The 2.4 GHz band is longer in wavelength and can cover larger distances but is often more prone to interference.
o The 5 GHz band is shorter in wavelength and provides faster speeds but works over shorter distances.
· Transmission: A Wi-Fi router emits radio waves in the form of signals. These signals are broadcasted through the air, and your Wi-Fi-enabled device detects and picks up these signals to communicate with the router.
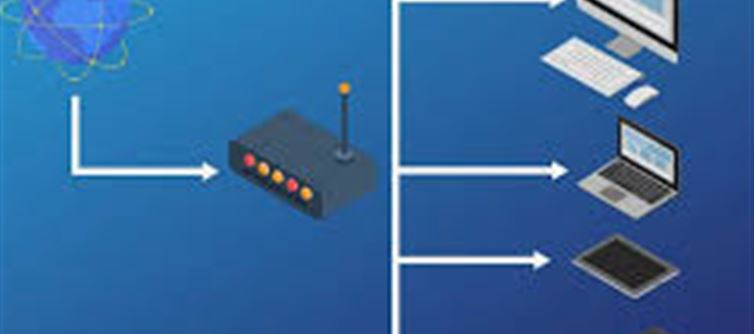
3. How Does the Router Connect to the Internet?
The key to Wi-Fi’s functionality is the router. Here’s how it works:
· Internet Connection: The router is connected to the internet via a wired Ethernet cable or fiber optic cable, which sends a continuous stream of data to the router from your Internet service Provider (ISP).
· Signal Transmission: The router takes that data and converts it into radio signals that are transmitted wirelessly to nearby devices.
4. What Happens Inside the Router?
A Wi-Fi router has several components that allow it to convert wired internet data into radio waves for wireless transmission.
· Modem: A router is typically paired with a modem, which is the device that brings the internet signal into your home via your internet connection. The router and modem work together to transmit internet data in wireless form.
· Antenna: Routers are equipped with antenna(s) that send and receive radio signals. Some modern routers have multiple antennas for stronger signals and greater range.
· Wi-Fi Standards: Wi-Fi routers comply with various Wi-Fi standards (like 802.11a/b/g/n/ac/ax), which define how efficiently the data is transmitted and received. Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) is the latest standard offering faster speeds, less congestion, and better range.
5. How Do Devices Connect to Wi-Fi?
When you want to connect your device (like a smartphone or laptop) to a Wi-Fi network, the device searches for available networks within range. Here’s how it happens:
· Search for Networks: Your device scans for Wi-Fi networks that are broadcasted by routers. These networks are identified by their SSID (Service Set Identifier), which is the network name you typically see when trying to connect.
· Authentication: Once you select your network, the device sends a request to the router to connect, and if the router has the correct password (if secured with WPA/WPA2 encryption), the device is allowed to join.
· Data Exchange: After connection, the router establishes communication with the device, transmitting internet data via radio waves. The data is broken down into small packets, transmitted over radio waves, and reassembled at the destination device.
6. Security Measures
Wi-Fi networks can be vulnerable to hacking or unauthorized access. To ensure privacy, Wi-Fi networks are usually secured with encryption protocols like WPA2 or WPA3.
· Encryption: This process scrambles the data sent over the network, so even if someone intercepts the signal, they cannot read the data.
· Password Protection: Most Wi-Fi networks require a password to connect, which adds an extra layer of security to prevent unauthorized users from accessing the network.
7. Why Is Wi-Fi So Convenient?
Wi-Fi is incredibly popular because it offers high-speed internet without the hassle of physical wires. Here’s why Wi-Fi is so effective:
· Mobility: Devices like smartphones, laptops, and tablets can connect to Wi-Fi anywhere within the router’s range, enabling mobility without losing internet access.
· Flexibility: It can serve multiple devices at the same time, making it ideal for homes and offices with many users. Routers can support dozens of devices simultaneously without degrading the speed significantly.
· Ease of Use: Setting up a Wi-Fi network is relatively simple. Once the router is installed and configured, all your devices can automatically connect to it as long as they are within range.
8. The Future of Wi-Fi Technology
Wi-Fi technology continues to evolve with new standards like Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E, which promise faster speeds, lower latency, and better performance in crowded environments.
· Wi-Fi 6 offers higher speeds, better efficiency, and the ability to handle more devices simultaneously, which is especially important as homes become more connected with IoT devices.
· Wi-Fi 6E extends the capability of Wi-Fi 6 into the newly available 6 GHz band, offering even more capacity and speed.
Conclusion: The Magic of Wireless Internet
Wi-Fi might seem like a mysterious technology that lets us access the internet wirelessly, but it’s all thanks to radio waves, routers, and advanced encryption techniques that make this possible. By converting wired internet data into radio signals, Wi-Fi allows us to enjoy the freedom of mobility and connectivity without the limitations of wires.
So, the next time you connect to Wi-Fi, you’ll know exactly how it works and what’s happening behind the scenes to keep you online, wire-free!
Disclaimer:
The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of any agency, organization, employer, or company. All information provided is for general informational purposes only. While every effort has been made to ensure accuracy, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, reliability, or suitability of the information contained herein. Readers are advised to verify facts and seek professional advice where necessary. Any reliance placed on such information is strictly at the reader’s own risk..jpg)




 click and follow Indiaherald WhatsApp channel
click and follow Indiaherald WhatsApp channel