Monkeypox, a viral zoonotic disease, has emerged as a public health concern in several countries. While it is less contagious than some other viral infections, the virus can still spread through close contact with infected individuals or contaminated objects. Understanding preventive measures is essential to protect yourself and your community.
What is Monkeypox?
Monkeypox is caused by the Monkeypox virus, a member of the orthopoxvirus family. The infection typically manifests with:
Fever and chills
Headache and muscle aches
Swollen lymph nodes
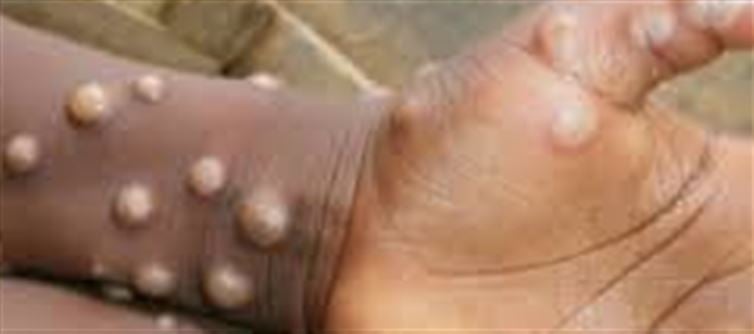
Rash, often beginning on the face and spreading to other body parts
While most cases are mild, vulnerable populations—such as children, immunocompromised individuals, and pregnant women—can experience severe illness.
How Monkeypox Spreads
Monkeypox primarily spreads through:
Direct contact with the lesions, body fluids, or scabs of an infected person
Respiratory droplets during prolonged face-to-face contact
Contaminated objects such as bedding, clothing, or personal items
Understanding these transmission pathways is crucial for effective prevention.
Essential Guidelines to Avoid Infection
1. Practice Good Hygiene
Wash hands frequently with soap and water for at least 20 seconds.
Use alcohol-based hand sanitizers when soap and water are not available.
Avoid touching your face, especially eyes, nose, and mouth, with unwashed hands.
2. Avoid Close Contact with Infected Individuals
Refrain from hugging, kissing, or sharing personal items with someone showing symptoms.
Infected individuals should isolate until fully recovered, typically 2–4 weeks.
3. Disinfect Contaminated Surfaces
Clean commonly touched surfaces, such as doorknobs, phones, and bathroom fixtures, with disinfectants.
Wash bedding, towels, and clothing of infected persons separately in hot water.
4. Practice Safe Sexual Behavior
Monkeypox can be transmitted through close skin-to-skin contact during sexual activity.
Use protective measures and avoid sexual contact if you or your partner show symptoms.
5. Protect Yourself in High-Risk Environments
Healthcare workers should use personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, masks, and gowns, when caring for infected patients.
Avoid contact with wild animals that may carry the virus, especially in endemic areas.
6. Monitor Your Health
Be vigilant for symptoms such as fever, rash, and swollen lymph nodes, especially after potential exposure.
Seek medical advice promptly if you suspect infection. Early detection helps prevent the spread.
7. Vaccination and Immunity
In some countries, smallpox vaccines are recommended for high-risk groups, as they provide protection against monkeypox.
Consult healthcare professionals for advice on vaccination if you are in a high-risk area or profession.
Additional Preventive Tips
Educate yourself and your family about monkeypox symptoms and transmission.
Avoid contact with unknown animals or individuals exhibiting unusual rashes.
Maintain a healthy immune system through proper nutrition, sleep, and stress management.
Conclusion
While monkeypox is a serious infectious disease, it can be effectively prevented with careful hygiene, responsible behavior, and awareness of transmission risks. By following these essential guidelines, you can significantly reduce your risk of infection and help protect the wider community.
Remember, early detection, isolation, and preventive measures are the most effective tools against the spread of monkeypox. Staying informed and vigilant ensures safety for yourself and those around you.
Disclaimer:
The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of any agency, organization, employer, or company. All information provided is for general informational purposes only. While every effort has been made to ensure accuracy, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, reliability, or suitability of the information contained herein. Readers are advised to verify facts and seek professional advice where necessary. Any reliance placed on such information is strictly at the reader’s own risk.




 click and follow Indiaherald WhatsApp channel
click and follow Indiaherald WhatsApp channel