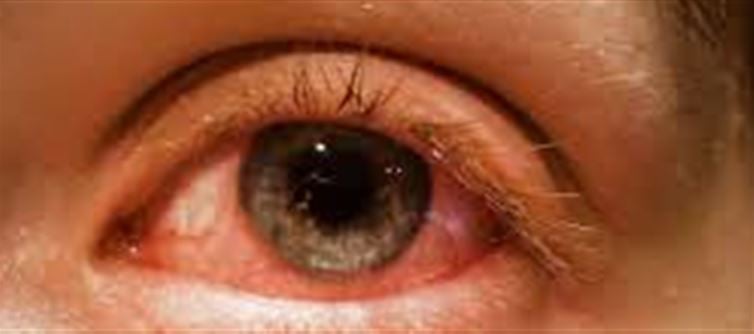
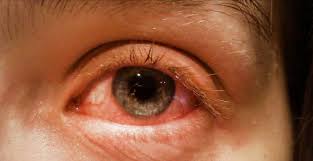
Waterborne eye infections are ocular conditions caused by pathogens—such as bacteria, viruses, or parasites—present in contaminated water sources. These infections can occur when water containing harmful microorganisms comes into contact with the eyes, leading to various symptoms and potential complications.
Common Causes and Symptoms
Common pathogens responsible for waterborne eye infections include Acanthamoeba, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Chlamydia trachomatis. Symptoms may vary depending on the specific pathogen but often include:
- Redness and irritation
- Excessive tearing or discharge
- Swelling of the eyelids
- Pain or sensitivity to light
- Blurred vision
In severe cases, untreated infections can lead to corneal ulcers or permanent vision loss.
Risk Factors
Individuals at higher risk for waterborne eye infections include:
- Contact lens wearers, especially those who swim or use lenses improperly
- People with compromised immune systems
- Individuals who frequently swim in untreated or poorly maintained water bodies
Prevention Strategies
To protect against waterborne eye infections:
- Wear protective eyewear: Use well-fitting goggles to prevent water from entering the eyes during swimming.
- Maintain good hygiene: Wash hands thoroughly before touching the eyes or handling contact lenses.
- Avoid swimming in untreated water: Refrain from swimming in lakes, rivers, or pools with questionable water quality.
- Proper lens care: Follow recommended cleaning and storage procedures for contact lenses.
- Seek medical attention promptly: Consult an eye care professional if symptoms of an eye infection occur.
Treatment Options
Treatment for waterborne eye infections depends on the causative organism and the severity of the condition. Options may include:
- Topical antibiotics or antifungal medications: To treat bacterial or fungal infections.
- Antiviral medications: For viral infections, as prescribed by a healthcare provider.
- Oral medications: In severe cases, systemic treatment may be necessary.
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent complications and preserve vision.
If you have further questions or need more information on this topic, feel free to ask.




 click and follow Indiaherald WhatsApp channel
click and follow Indiaherald WhatsApp channel