
Indian astronaut Shubhanshu Shukla will be released to the international Space Station on CAN also 29. He'll be riding aboard the SpaceX Dragon spacecraft that he will pilot along with the Axiom-4 challenge team.
Onboard the Dragon spacecraft,
A set of new experiments might be launched to be performed inside the vacuum of area. Amongst those experiments, a brand new look ought to forever change space travel.
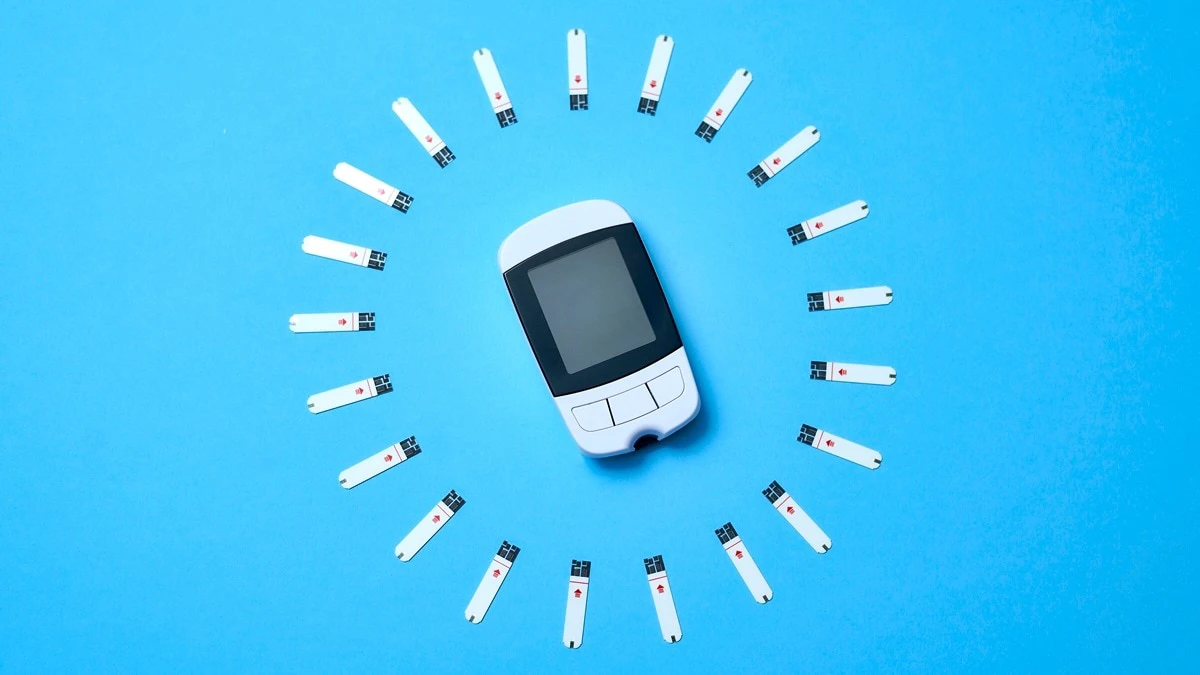
For decades, human beings with diabetes have been advised they couldn't emerge as astronauts. The threat of handling blood sugar in the area changed into being taken into consideration too high. However, a new challenge known as 'Suite experience' could alternate that after Ax-4 astronauts check it in zero gravity.
What's 'SUITE ride'?
'Suite trip' is a research venture at the Axiom Venture Four (Ax-4) to the international Space Station (ISS). Its goal is to discover secure methods for human beings with insulin-based diabetes to live and work in space.
The assignment focuses on 3 main obligations:
Accurate blood sugar tracking: ensuring devices can reliably measure blood sugar ranges in space.
Information collection in orbit: gathering actual-time blood sugar information from astronauts aboard the ISS.
Ground evaluation: Sending the records returned to Earth so doctors can study it and make sure of safety.
by completing those steps, 'Suite journey' objectives to show that managing diabetes in area is possible, starting the door for diabetic
candidates who aspire to come to be destiny astronauts.
INDIA'S position inside the mission
group Captain Shubhanshu Shukla of the indian Air Force is a key member of the Ax-4 team. He'll behavior existence science experiments at the ISS. He may also probably be celebrating the 'Suite Journey' experiment.
Shukla's participation highlights India's developing involvement in space exploration.
But Axiom has no longer disclosed which astronauts will solely take a look at the brand new
test once they dock with the distance station.
WHY is this a leap forward?
traditionally, individuals with insulin-established diabetes were excluded from area missions due to issues over managing the circumstance in microgravity. But recent research has shown promising outcomes:
Insulin pump performance: Research carried out by Kyle Horn has proven that insulin pumps function successfully in microgravity, keeping consistent fluid shipping without considerable variations throughout numerous gravity situations.
Centrifuge Simulations: Assessments involving kind 1 diabetic subjects with insulin pumps exposed to simulated spaceflight situations showed no destructive clinical responses, suggesting that individuals with diabetes would possibly tolerate the stresses of area tours.
Those findings assign long-status assumptions and indicate that with the proper era and protocols, managing diabetes in space is possible.
The Ax-four team will launch on May 29.
the larger photograph
The implications of 'suite experience' make it bigger beyond space exploration. Improvements in clinical technologies for area missions can lead to advanced healthcare answers on earth, in particular in faraway or resource-confined settings.
As an example, lightweight, transportable diagnostic gadgets advanced for astronauts may be adapted to be used in rural healthcare facilities.
Reading glucose metabolism in the area affords important insights into insulin sensitivity, metabolic edition, and far-flung monitoring, advancing
both astronaut health and diabetes care in the world.
"At Burjeel Holdings, we're committed to reworking those findings into progressive treatments for our patients," said Dr. Mohammad Fityan, chief medical officer at Burjeel Clinical Metropolis and scientific lead of the suite trip look at.
Furthermore, this initiative sets a precedent for re-evaluating scientific disqualifications in diverse excessive-stakes professions, selling a more inclusive approach based on personal exams rather than blanket exclusions.
If 'Suite ride' succeeds, it is able to cause modifications in astronaut selection criteria, allowing individuals with properly managed diabetes to enroll in destiny missions.
This development now has the handiest advantages.
Aspiring astronauts, however, also demonstrate how space research can result in clinical advancements that improve lives on earth.




 click and follow Indiaherald WhatsApp channel
click and follow Indiaherald WhatsApp channel